The diagnostic reference level (in terms of volume CTDI) is 75 mGy. The pass/fail limit (in terms of volume CTDI) is 80 mGy. These values are for a routine adult head exam and may be significantly different (higher or lower) for a given patient with unique indications. NOTE: All volume CTDI values are for the 16-cm diameter CTDI phantom.. principles for performing high-quality CT imaging of the brain in pediatric and adult patients, including advanced applications such as CT perfusion, CT volumetry, CT angiography, and CT venography. II. INDICATIONS Indications for CT of the brain include, but are not limited to: A. Primary Indications 1. Acute head trauma. 2.

Dynamic, ContrastEnhanced CT of Human Brain Tumors Quantitative Assessment of Blood Volume

CT head without contrast showing a thin, predominantly lowdensity... Download Scientific Diagram

When a plain CT brain looks like contrastenhanced never polycythemia BMJ Case Reports
Brain Ct Scan Report Sample Pdf barebonestory

Computed tomography scan of brain (plain and contrast) Download Scientific Diagram

Figure 3. Head Ct Scan With Contrast Showed The Lession By The Red B2E

Brain Jack Image Brain Ct Scan

CT brain with contrast ACA Aneurysm finding YouTube
CT With Contrast and MRI With Contrast Facts to Know • Touchstone Medical Imaging

Preoperative CT brain with contrast in axial (A), coronal (B), and... Download Scientific Diagram

CT Brain with Contrast of a Stroke Patient Stock Photo Image of head, black 154760818

อัลบั้ม 102+ ภาพพื้นหลัง Ct Brain Contrast Vs Non Contrast คือ คมชัด
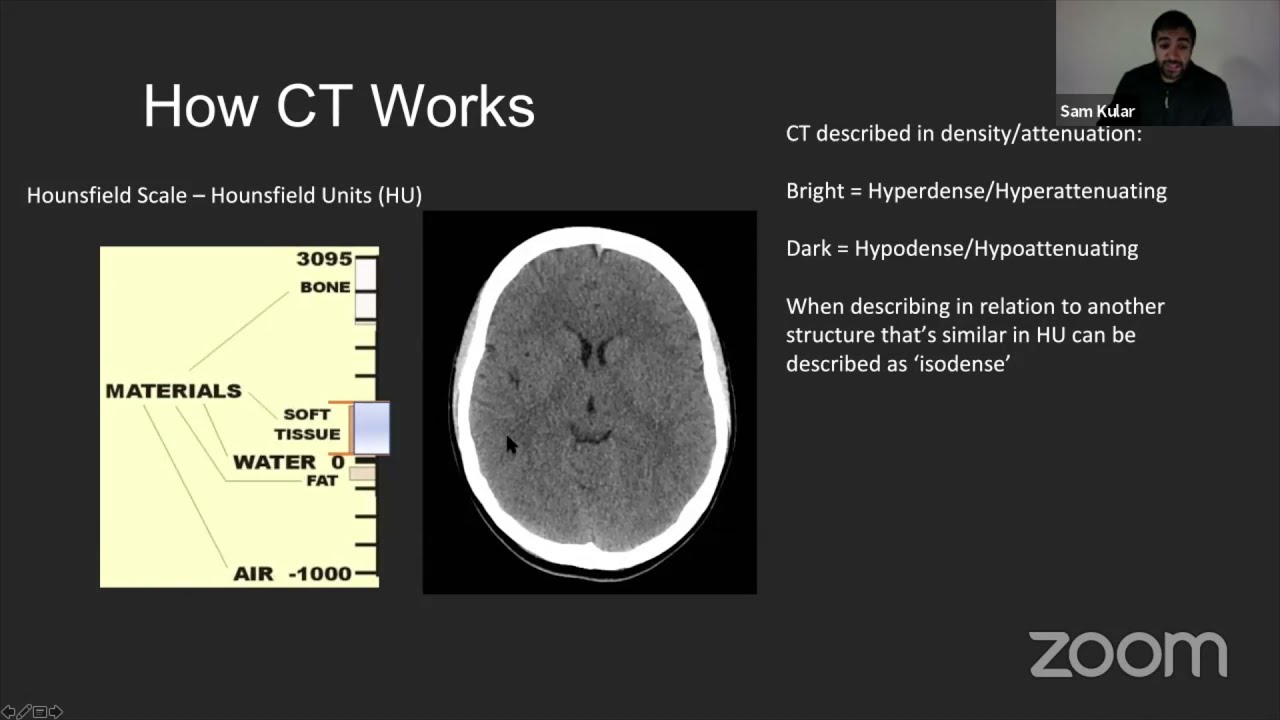
CT head Interpretation YouTube

CT head with contrast shows swelling and enhancement of the front... Download Scientific Diagram
CT brain image gallery Meningioma
CT vs MRI How Can You Tell The Difference? Faculty of Medicine

CT brain scan with sagittal and axial views. Day 1 CT brain normal.... Download Scientific

What is a brain CT scan? Two Views

Contrastenhanced axial brain CT images of case 1. Multiple metastases... Download Scientific
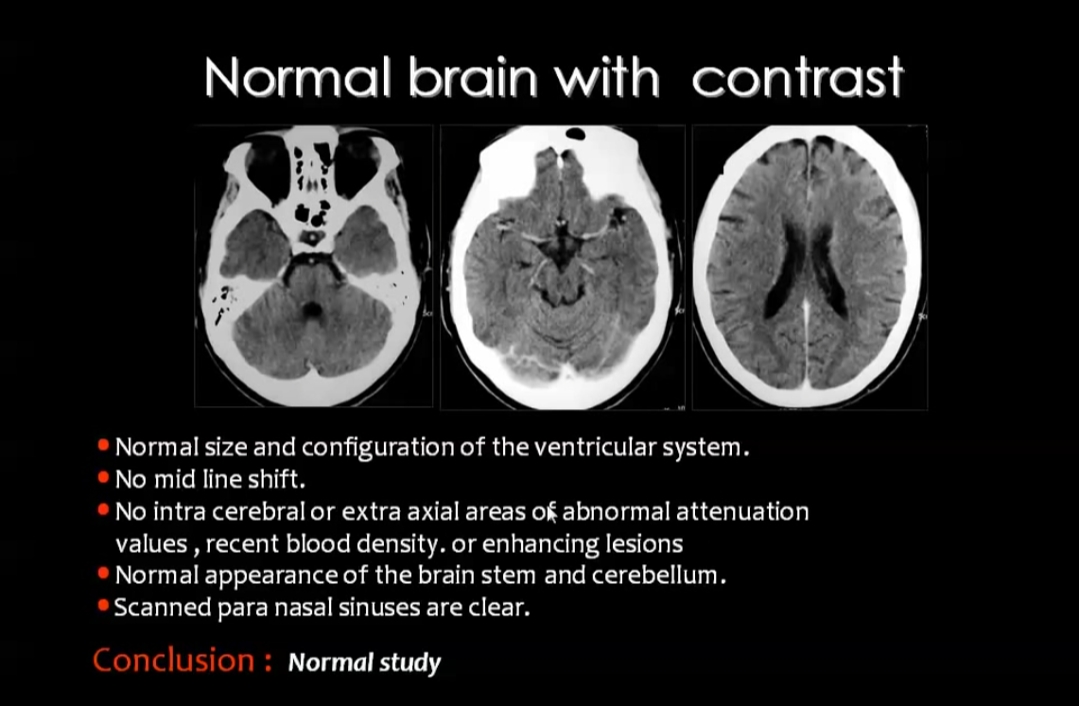
case study Normal CT brain with contrast How to report
Head CT. Computed tomography (CT) of the head uses special x-ray equipment to help assess head injuries, severe headaches, dizziness, and other symptoms of aneurysm, bleeding, stroke, and brain tumors. It also helps your doctor to evaluate your face, sinuses, and skull or to plan radiation therapy for brain cancer.. Non-contrast studies of the brain and spine are sufficient for most indications. Diagnosis of common conditions such as cerebral infarction and haemorrhage can be made without intravenous contrast. A contrast-enhanced CT of the brain is of value in specific situations (eg known CNS tumour, investigation for potential intracranial metastases.